Last Updated on March 11, 2024 by admin
Proportional and Fixed Costs
Applying the cost cube from the previous post means that for decision support all costs have to be split into their proportional and fixed portion, since proportional is the consequence of units produced and sold, fixed is the consequence of management decisions. The point is to correctly represent the principle of cause and effect in cost center planning. This splitting is done in the planning process.
-
- An employee in a production center can work on production orders (setup, production, monitor quality, pack finished parts into transport containers). These are tasks that are causally necessary for the creation of a defined product. Without them, the product cannot be created. They are incurred proportionally to the quantity produced. The same employee can organize, take part in further training, attend meetings, clean up the workplace or, hopefully in rare cases, wait for work. The latter activities are determined by the organization of the cost center. They are incurred independently of the quantity produced and are therefore part of the cost center’s fixed costs.
- The consumption of electrical energy in a production cost center is mainly determined by the type of product to be manufactured and the quantity produced. Electricity is also consumed for lighting, air conditioning, and the operation of auxiliary equipment such as computers. The consumption for production is causally necessary for the creation of the product and must therefore be planned proportionally. The rest of the electricity consumption is again the part of the capability to perform.
- Maintenance work on the machines installed in the cost center can be caused by the operation of the equipment, e.g. after 200 hours of operation the rollers have to be replaced because they are no longer flat. Other maintenance work (technical inspections, functional checks) is due after a predetermined period of time, for example, annually, regardless of the quantities produced, to ensure operational readiness.
The examples show that different cost elements in a cost center must be planned with a proportional and a fixed portion. The following section shows how the necessary cost splitting can be largely automated. The example of the Stamping cost center is reused for this purpose.
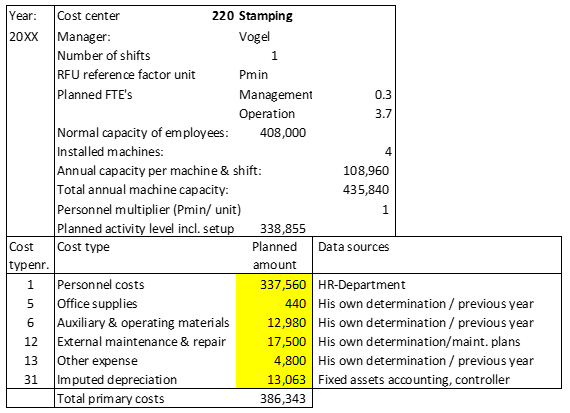
In comparison to the initial situation in the post “Planning Cost Centers”, the columns proportional, fixed and value consumption per RFU have been added.
The procedure for automated cost splitting using the example of personnel costs: The annual budget for personnel costs is 337,560. This amount divided by the normal capacity of the employees (408,000 Pmin) results in the average presence time rate per minute of 0.82735. This is the average cost per minute “been there” of any employee in this cost center. The 0.82735 are multiplied by the planned activity level of 338,855 Pmin. The planned proportional personnel costs are thus 280,353. The fixed costs are the difference to the planned amount (57,207).
For the other cost types the cost center manager considers for each of these what portion of the planned amount depends on the cost center’s activity. In the example, these are the consumption of auxiliary and operating materials, external maintenance, other expense, and energy. The manager derives this proportional share from his planning documents (maintenance contracts, consumption tables for energy, material costs that only arise from productive work). By dividing the amount by the planned activity he receives the consumption per reference factor unit (RFU, entry in last column). Since the RFU in the stamping shop is the minute, this naturally results in very low rates. The calculation method is then analogous to the splitting of the personnel costs.
Tip for practical implementation: Do not use percentages when splitting the proportional from the fixed amount. Always use the proportional rate per RFU. If the planned activity level has to be adjusted due to a changed production plan, the proportional plan cost rate of the cost center would change when using percentages. This is unrealistic because it is still the same product with the same work plan.
Cost splitting is a prerequisite for the calculation of proportional planned product costs. In order to be able to process if-then questions, the manager must know which costs are directly caused by the product (proportional planned production costs) and which cost blocks are the result of structural and capacity decisions (fixed costs). The latter change as shown in the cost cube through management decisions while the proportional product costs per unit remain the same as long as the product unit has the same bill of materials and work plan.
If the planned activity level, the planned cost amounts per cost type and the consumption per RFU are known for each cost center, cost splitting can be completely automated. Proof of this is provided in the simulation model of the book Management Control with Integrated Planning – Models and Implementation for Sustainable Coordination.
Cost splitting is not necessary in structure cost centers since these areas work for the products and not on the products. Consequently, only fixed costs can be planned in these cost centers.
