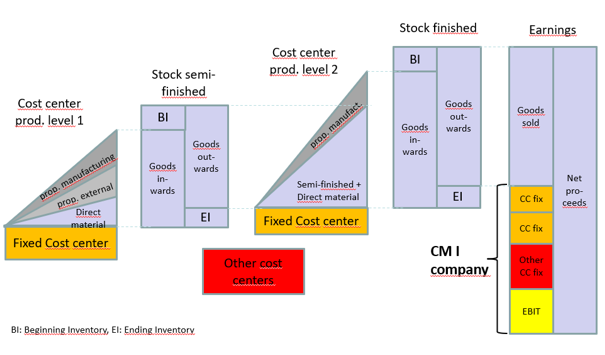
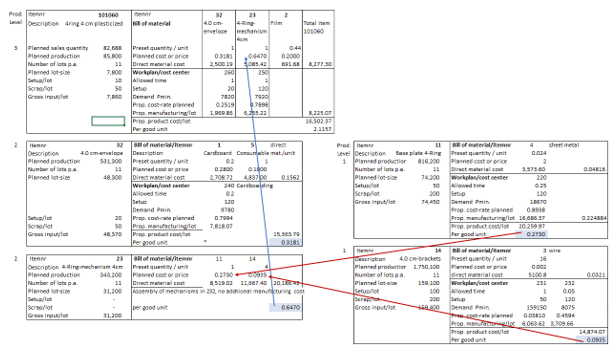
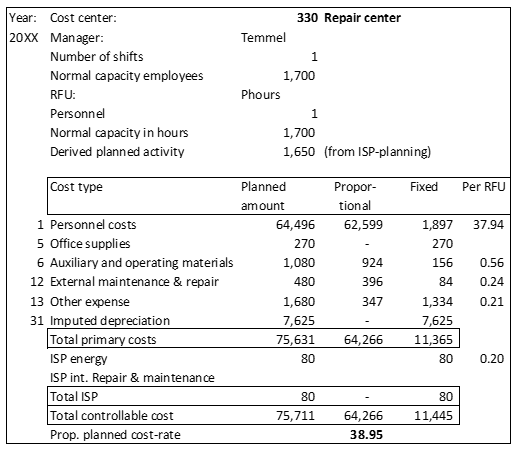
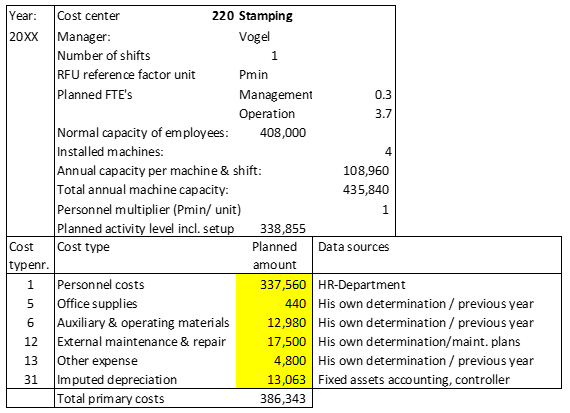
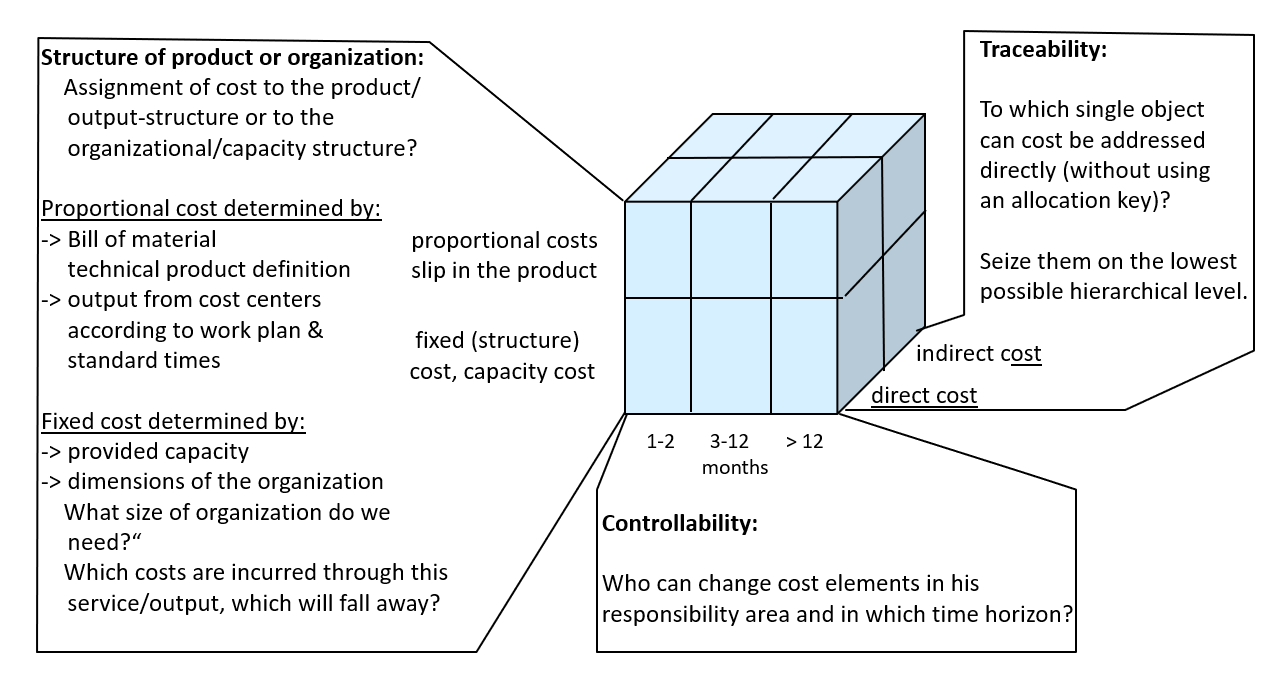
Corner stones for the implementation of the decision-relevant Management Accounting System covering revenue, activities, capacities, cost and earnings.
Management Tasks and Management Accounting
The design of the management accounting system outlined in this blog and in the book “Management Control with Integrated Planning” is based on generally accepted management principles and the resulting behaviors.
Decision support and responsibility for results
All managers make decisions and are responsible for their implementation. This applies to all individuals who manage an area and are accountable for its results to their superiors or to the company. Managers of all levels are thus the main customers of the management accounting system. Consequently, such systems must be structured to provide decision support to all managers at all management levels and to delineate responsibilities in a manner that is appropriate to the organization.
To fulfill its purpose, results must be achieved by a company. Objectives are results to be achieved. Each manager should be able to plan, measure and control the achievement of his objectives in accordance with his responsibilities.
As far as monetary targets are concerned, they are to be described in the management accounting system. From this it can be deduced that planning in management accounting should run in parallel with the process of agreeing on objectives. If, for example, the activity quantity of a cost center is determined as a target, but the headcount required for this objective is not approved, it cannot be achieved.
Objectives and plans belong together
When planning, it is necessary to make and prepare the decisions regarding personnel, material and financial resources required to meet the strategic and the operational goals. Since this process is time-consuming, ways are often sought to simplify and shorten the planning process. Despite the large amount of work involved, however, practice shows that it is worthwhile to plan all areas, products and management levels once a year in terms of performance and value and in conjunction with the objectives of an area. This provides the benchmark for the plan to target and plan to actual comparison and thus the basis for determining corrective actions. Planning for a fiscal year also proves useful in “short-lived” times, because personnel and management decisions as well as objectives are usually also agreed for a fiscal year.
The management cycle requires plan, target and actual data
In order for the management cycle to work properly the plans that are created together with the objectives must be stored in the system in all their detail, so that they can be compared with the results achieved. The comparison of planned, target and actual data makes it possible to also measure the actual extent of achievement of the objectives in monetary values. It is recommended to prepare the plan to actual comparison on a monthly basis, so that the real events are still present for the evaluation of the results. It also enables faster reaction in the case of unfavorable variances. For projects, the plan to actual comparison should also be set up for each milestone, because at each milestone meeting a decision has to be made as to whether the project should be continued or terminated (a go/no-go decision).
Managers at all levels usually decide on quantities, activities and times. The value consequences of implementation then become known in cost accounting. This requires that the management accounting system be designed as a cost-, activity-, revenue- and earnings system (CARE). Management-oriented CARE is therefore clearly distinguished from purely money-based financial accounting.
Requirements from strategic and medium-term planning
Strategic planning defines the intended positioning in the markets. For this purpose, product/market positions to be achieved are specified with quantities and revenues for several years.
Medium-term operational planning has the task of preparing the implementation of the strategies. Since the managers must record quantities, services and prices for this purpose, the CARE structures must also be set up in the multi-year planning.
In annual planning, the planned purchase prices, the planned personnel costs, and the bills of materials as well as the work plans for the planned year are set. This results in new planned cost center rates and new planned product costs.
Adjustments at the beginning of the new year
To enable managers to compare their achieved results with the planned values at any time during the year, the inventories of materials, semi-finished and finished products in CARE must be revalued using the new approach at the beginning of the next year.
If, for example, a product can be manufactured at a lower cost in the new year due to a process improvement, the previous year’s ending inventory must be revalued internally with the new cost rates. If this revaluation of the year-end inventory is not carried out, variances will occur in the new year which still belong to the old year. This revaluation is only carried out in management accounting and can be automated. Inventory valuation for financial accounting continues to follow the applicable commercial law regulations.
Forecasts
Because the preparation of forecasts ties up a lot of management capacity, it is advisable to schedule two forecast dates. When the fiscal year corresponds to the annual calendar, the first forecast should be prepared on the basis of the planned and actual data from January to April (Easter days are then always included). Based on the accumulated actual values as of the end of August (major vacation period mostly completed), the second forecast should be prepared. This forecast also serves as the input for the subsequent planning of the next business year. Stock-listed companies are usually forced to prepare quarterly forecasts. However, practice shows that especially forecasts based on the actual data as of the end of March is not very meaningful, and its preparation usually causes a lot of hectic activity in the organizations.
Controllers check the right system application
As designers and operators of the management accounting system, controllers have the task of monitoring the correct application of the planning and controlling system. This results from the controller mission statement (see Management, Controlling, Controller). Once the planning results or forecast data have been entered into the management accounting system, a sufficient period of time must be provided during which the controllers can check compliance with the system rules and, if necessary, ensure that corrections are made on time. Unfortunately, there are always “specialists” who try to abuse the planning system or valuation rules in their favor by circumventing content-related or process-related rules:
-
- In a company known to us, a business unit manager massively manipulated the planned net attendance times of the employees in order to be able to calculate lower unit costs in the plant he wanted to erect. On this basis, the investment in the plant was approved by the group’s management. In the first year of operation it already became apparent that the actual attendance times did not correspond to the planned ones, which led to the loss of the planned cost savings. In retrospect, the desision to make the investment had to be judged as wrong, but the money had already been spent.
- In multinational companies, there is a great risk that decisions about the profitability of a subsidiary are made on the basis of transfer prices between group companies. However, the latter are driven by international transfer pricing regulations obeying legal requirements and leaving out the overall group view (each country wants to generate taxes locally for the value produced, making it difficult to properly charge group services back to the producing and selling individual companies).
- From a controllers’ view, planning for an individual company must therefore be based on local conditions, but must also take into account the group’s internal planning and control requirements (those parameters which the local managers can actually influence themselves and therefore also take responsibility for). From this it can be deduced that controllers must set up the management accounting system in such a way that the entire business can successfully be managed locally. The finance department at corporate headquarters, on the other hand, must use transfer pricing to ensure that the overall corporate tax burden remains as low as possible (tax optimization). From a management perspective, these two areas must be kept separate if local planning and management are to be carried out correctly and the group result optimized.
Design of the decision-relevant Management Accounting System
To design a comprehensive management accounting system that can meet the requirements resulting from the management process, we have been observing the scientific developments as well as their practical implementations at our customers for several decades. According to our findings, the following sources and systems are of decisive importance for the design of CARE:
-
- Marginal costing according to Hans-Georg Plaut (Grenzplankostenrechnung GPK)
- Standard costing with flexible budgets according to Wolfgang Kilger
- Contribution margin accounting according to Albrecht Deyhle
- Sales and turnover planning according to the lived market cultivation structures
- Extension to multi-level and multi-dimensional contribution margin accounting (mainly described by Lukas Rieder)
- Three dimensions for the management-oriented structuring of costs and revenues in the controller dictionary of the International Group of Controlling (IGC)
- Activity Based Costing (ABC) according to Robert Kaplan and Peter Norton, but without allocation of fixed costs (including capacity costs) to product units. This mainly corresponds to Resource Consumption Accounting (RCA)
- The Costing Levels Continuum Maturity Model by Gary Cokins
- The IMA (Institute of Management Accountants) Conceptual Framework for Managerial Costing.
References to these publications can be found in the bibliography of this blog.